

Received: AugAccepted: FebruPublished: March 30, 2023Ĭopyright: © 2023 Williams et al. PLoS Biol 21(3):Īcademic Editor: Maiken Nedergaard, University of Rochester Medical Center, UNITED STATES (2023) Neural activity induced by sensory stimulation can drive large-scale cerebrospinal fluid flow during wakefulness in humans. These results demonstrate that neural activity can contribute to driving CSF flow in the human brain and that the temporal dynamics of neurovascular coupling can explain this effect.Ĭitation: Williams SD, Setzer B, Fultz NE, Valdiviezo Z, Tacugue N, Diamandis Z, et al. The timing and amplitude of CSF flow was matched to the visually evoked hemodynamic responses, suggesting neural activity can modulate CSF flow via neurovascular coupling. We manipulated neural activity with a flickering checkerboard visual stimulus and found that we could drive macroscopic CSF flow in the human brain. To test whether the temporal coupling between neural activity and CSF flow is in part due to a causal relationship, we investigated whether CSF flow could be induced by driving neural activity with intense visual stimulation. While it is well established that CSF flow is modulated by respiratory and cardiovascular dynamics, recent work has also demonstrated that neural activity is coupled to large waves of CSF flow in the ventricles during sleep.
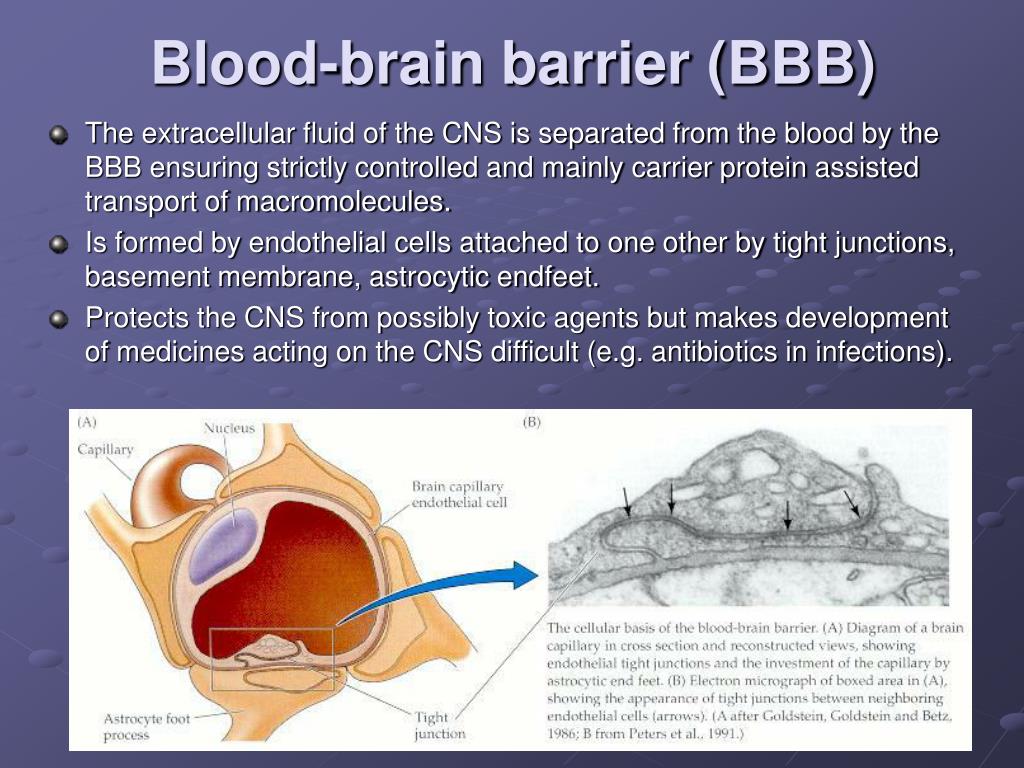
CSF flow is thus important for brain health, but the mechanisms that control its large-scale movement through the ventricles are not well understood. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow maintains healthy brain homeostasis, facilitating solute transport and the exchange of brain waste products.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
